Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a metric that is used to quantify the success of a process step or action. Key Performance Indicator Models (KPIMs) incorporate KPIs into a process flow to help add priority information around the requirements, with are connected to the process step the KPI references.
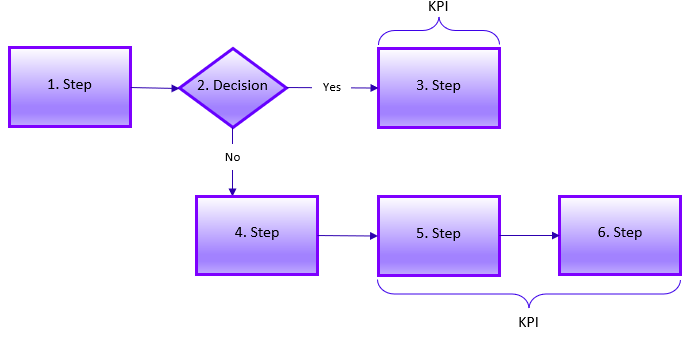
This model is generally layered on top of a Process Flow or a System Flow. The purpose of a KPIM is to help better understand the KPI as it relates to a particular step or group of steps. Most often, KPIMs are used on projects where a well-known, existing software will be replaced, and the unknown replacement is causing some anxiety to the stakeholders involved. This model helps stakeholders visualize the improvements they will experience once the new system is in place.
Key Performance Indicator Models are also used from a testing perspective. The improvement the system, and its users, will experience is clearly shown within the model, and can be referred back to as a way to measure successful implementation.
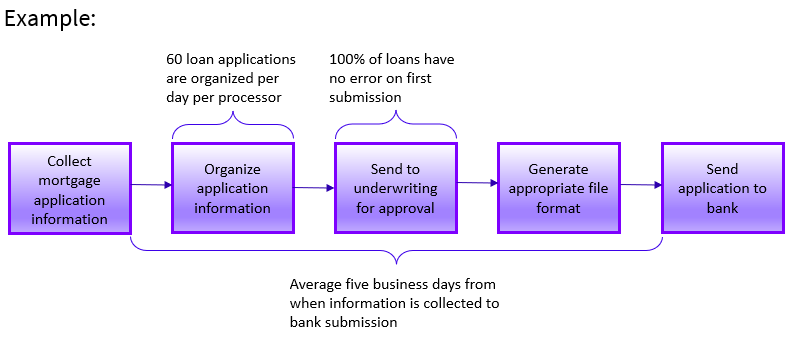
For more information on choosing the right KPIs when automating a business process, visit Business Process Automation Metrics.
Learn more about requirements models in our book Visual Models for Software Requirements (Microsoft Press, 2012) Joy Beatty and Anthony Chen. (See Chapter 5 for Key Performance Indicator Models)